Hybrid automation - human in the loop
Hybrid Automation is only available on paid plans.
Hybrid automation enables seamless collaboration between automated scripts and human users, allowing manual intervention when needed for tasks like credential input, 2FA handling, or complex interactions. This works with Puppeteer, Playwright, and any library supporting CDP connections.
How It Works
When creating a liveURL in our Chrome DevTools API, Browserless will return a one-time link to a webpage which you can share with your end-users. No API tokens or other secretive information is shared in this link, and no additional software or third-party packages are required.
By default, this feature intends to mimic the underlying browser's screen to your end users, and will adjust the underlying browser to "fit" your end-users screen. As an example: If your user has a screen of 1920x1080, then we'll resize the underlying browser to match. This is configurable by specifying a value of resizable: false when creating this URL, which will preserve whatever viewport the browser currently is.
Interactions with the page are also turned on by default. This means your end user can click, type, scroll, touch, or tap on the page and interact with the page. We use a compressed video stream to preserve as much bandwidth as possible, and you can also configure a quality option, with values of 1 - 100 to lessen the amount of network consumption. This is ideal for streaming to mobile devices.
Finally, by default only the relevant page from the browser is streamed, which means that if you have multiple tabs open, only the one that was used to create the liveURL will be streamed. If you want to stream all tabs, you can set the showBrowserInterface option to true, which will allow you to stream all tabs in the browser.
Key Features
- Real-time streaming: Compressed video stream with configurable quality (1-100)
- Interactive control: Users can click, type, scroll, and interact with the page
- Secure sharing: URLs contain no API tokens or sensitive information
- Flexible viewport: Automatically resizes to match user's screen or maintains fixed dimensions
- Event-driven: Listen for completion and CAPTCHA detection events
Basic Implementation
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
import puppeteer from 'puppeteer-core';
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: 'wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN_HERE',
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://example.com');
const cdp = await page.createCDPSession();
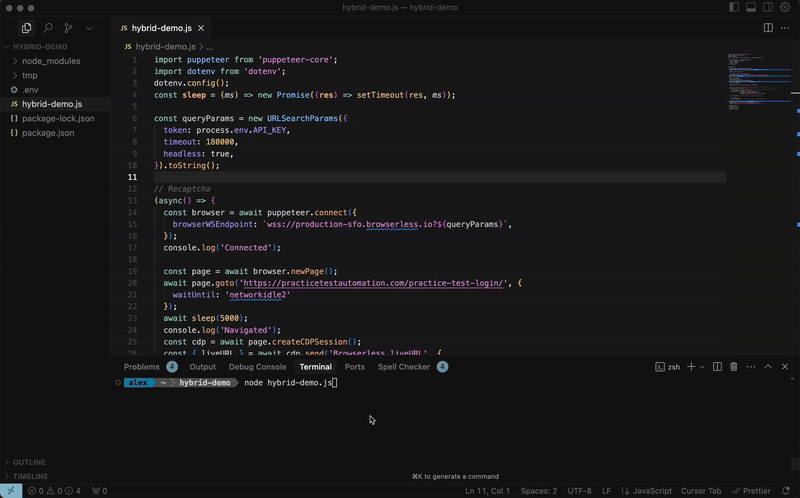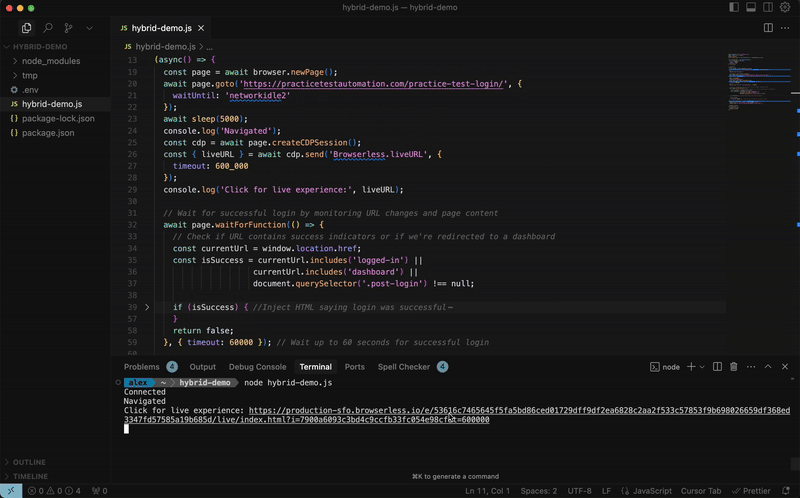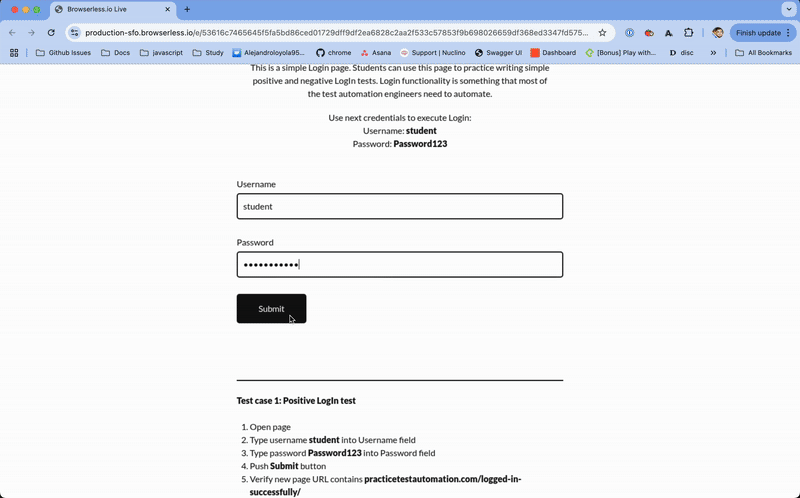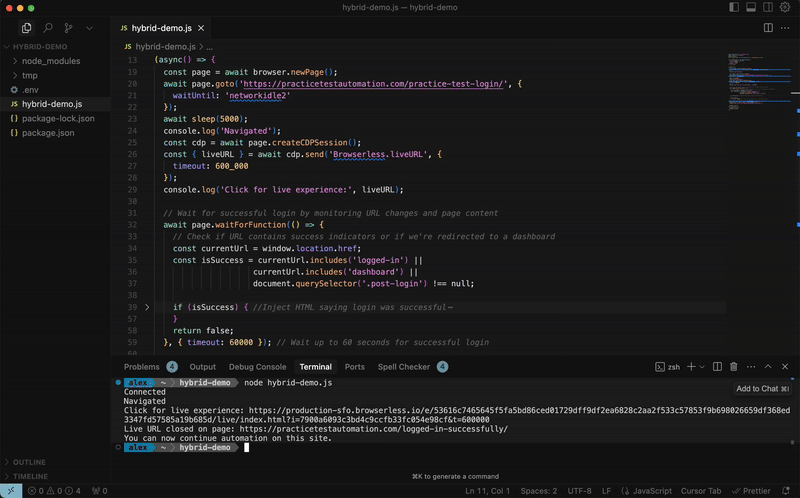
const { liveURL } = await cdp.send('Browserless.liveURL');
console.log('Share this URL:', liveURL);
// Wait for user to complete their tasks
await new Promise((r) => cdp.on('Browserless.liveComplete', r));
// Continue automation...
await browser.close();
import { chromium } from 'playwright-core';
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(
'wss://production-sfo.browserless.io/chromium/stealth?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN_HERE'
);
const [context] = await browser.contexts();
const page = await context.newPage();
await page.goto('https://example.com');
const cdpSession = await context.newCDPSession(page);
const { liveURL } = await cdpSession.send('Browserless.liveURL');
console.log('Share this URL:', liveURL);
// Wait for user to complete their tasks
await new Promise((r) => cdpSession.on('Browserless.liveComplete', r));
// Continue automation...
await browser.close();
Common Use Cases
Authentication and 2FA
Perfect for handling login flows that require human verification:
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
const login = async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.connect({
browserWSEndpoint: 'wss://production-sfo.browserless.io?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN_HERE',
});
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://accounts.google.com');
const cdp = await page.createCDPSession();
const { liveURL } = await cdp.send('Browserless.liveURL');
console.log('Please complete login:', liveURL);
// Wait for user to finish authentication
await new Promise((r) => cdp.on('Browserless.liveComplete', r));
// Continue with authenticated session
// Your automation code here...
await browser.close();
};
const login = async () => {
const browser = await chromium.connectOverCDP(
'wss://production-sfo.browserless.io/chromium/stealth?token=YOUR_API_TOKEN_HERE'
);
const [context] = await browser.contexts();
const page = await context.newPage();
await page.goto('https://accounts.google.com');
const cdpSession = await context.newCDPSession(page);
const { liveURL } = await cdpSession.send('Browserless.liveURL');
console.log('Please complete login:', liveURL);
// Wait for user to finish authentication
await new Promise((r) => cdpSession.on('Browserless.liveComplete', r));
// Continue with authenticated session
// Your automation code here...
await browser.close();
};
Multi-Tab Workflows
For workflows that involve multiple tabs or separate windows, you can enable the showBrowserInterface option when creating the liveURL. This will allow you to stream all tabs in the browser, enabling your end users to switch between them as needed. This is particularly useful for workflows that require multiple steps or interactions across different pages.
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
const { liveURL } = await cdp.send('Browserless.liveURL', {
showBrowserInterface: true, // Show all tabs and browser UI
quality: 50,
timeout: 300000, // 5 minutes for complex workflows
});
const { liveURL } = await cdpSession.send('Browserless.liveURL', {
showBrowserInterface: true, // Show all tabs and browser UI
quality: 50,
timeout: 300000, // 5 minutes for complex workflows
});
CAPTCHA Detection and Automated Solving
Combine automatic CAPTCHA detection with hybrid intervention. For basic CAPTCHA handling, see our CAPTCHA solving documentation:
- Puppeteer
- Playwright
// Set up CAPTCHA detection before navigation
cdp.on('Browserless.captchaFound', async () => {
console.log('CAPTCHA detected - attempting automatic solve');
// Try automatic solving first (see CAPTCHA docs for details)
const { solved } = await cdp.send('Browserless.solveCaptcha', {
appearTimeout: 20000
});
if (!solved) {
// Fall back to human intervention
const { liveURL } = await cdp.send('Browserless.liveURL', {
timeout: 120000 // 2 minutes for CAPTCHA solving
});
console.log('Manual CAPTCHA solving needed:', liveURL);
}
});
// Set up CAPTCHA detection before navigation
cdpSession.on('Browserless.captchaFound', async () => {
console.log('CAPTCHA detected - attempting automatic solve');
// Try automatic solving first (see CAPTCHA docs for details)
const { solved } = await cdpSession.send('Browserless.solveCaptcha', {
appearTimeout: 20000
});
if (!solved) {
// Fall back to human intervention
const { liveURL } = await cdpSession.send('Browserless.liveURL', {
timeout: 120000 // 2 minutes for CAPTCHA solving
});
console.log('Manual CAPTCHA solving needed:', liveURL);
}
});
Next Steps
Ready to explore more features? Continue your journey with these essential topics: