How to scrape websites
For web scraping, Browseless recommends using BrowserQL, our most advanced option. BQL is our own custom library that avoids the fingerprints left by other automation tools.
In this section you'll go through the following:
- How BrowserQL works
- Bypassing bot detectors
- Performing searches
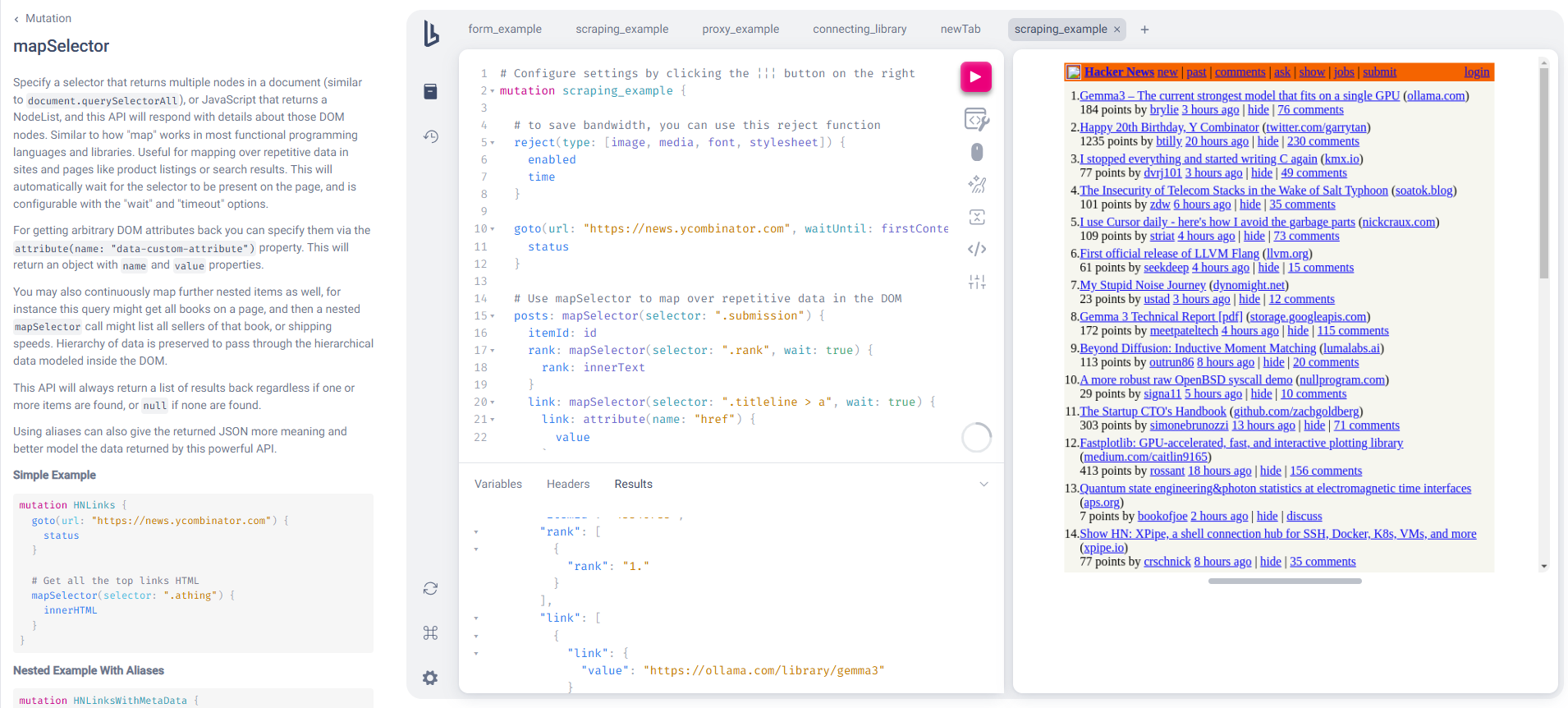
- Extracting HTML or a JSON
- Scraping responses
- Using API calls
- Connecting libraries
How BrowserQL works
BrowserQL is our own browser automation language, built on GraphQL. We’ve kept it simple, as a set of queries and responses.
BQL is optimized for web automation and scraping, designed to minimize complexity by making intelligent assumptions. Here’s what it does for you:
- Loads a browser with human-like fingerprints.
- Manages page-load events, like
firstContentfulPaint. - Handles proxies and request filtering.
- Waits for any mentioned selectors.
Instead of worrying about these technical details, you can focus on queries and actions. You will:
- Navigate to pages.
- Perform actions (e.g., click, type).
- Extract data (e.g., text, HTML).
Each query follows the format of function (arguments) {responses} with an optional name: beforehand For example, going to a site and grabbing a product name would be:
mutation scrape_example {
goto(url: "https://example.com", waitUntil: networkIdle) {
status
}
productName: text(
selector: "span#productTitle"
visible: true
) {
text
}
}
We then run this query with the browsers hosted in our cloud, which you can see run in the editor.